What is EMV?
EMV is a security framework that defines the payment interaction at the physical, electrical, data and application levels between chip cards and payment devices. These interactions are often referred to as EMV Level 1 and 2 requirements. EMVCo was created by the payment networks to be a neutral party in making this standard framework.
How Does it Work?
Smart cards are embedded with a chip that is encrypted with data. EMV-enabled devices have the ability to read data stored on a chip within the card. During the transaction authorization process, strong cryptographic functions are used to validate the authenticity of the card and cardholder.
Best of all, when a customer pays using an EMV-enabled device, the device is instantly identified as an authentic, approved payment instrument through a process called dynamic authentication. When used with a PIN, the chip proves that the customer is paying with his or her own card.
By using chips as an active part of the payment transaction, EMV cards and devices help prevent credit card fraud from stolen account numbers and cloned payment cards.
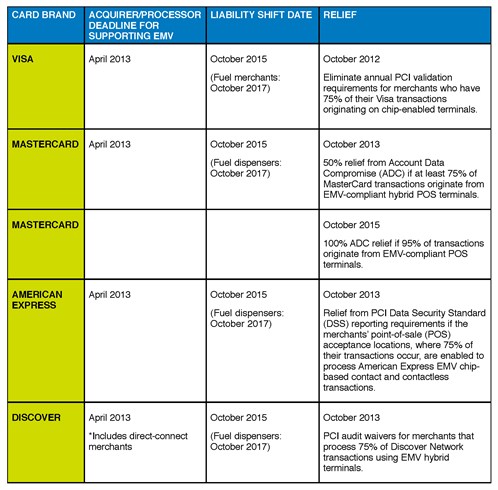
What do the dates mean?
Payment card networks in the US have provided guidance on how EMV is to be implemented and the incentives associated with migration to EMV for all payment card participants which includes merchants, acquirers and issuers. The key date chart provides a summary of those incentives.


